Power outages are among the calamities from which Texas surely suffers, with extents of interference ranging from immediate to prolonged, and may altogether mitigate nuisances under the canopy of weather conditions. The Texas Power Outage Map is a crucial tool for residents, businesses, and emergency response teams during crises, as well as for those working to restore power. This blog delves deeper into the factors leading to power outages in Texas, their far-reaching effects on communities, and some essential resources that help Texans stay informed and prepared. Whether you want to understand the weaknesses of the power grid or need practical ways to protect yourself from outages, this will prepare you to work around them. So, stay tuned for more in-depth information regarding these important matters.
Understanding Power Outages in Texas
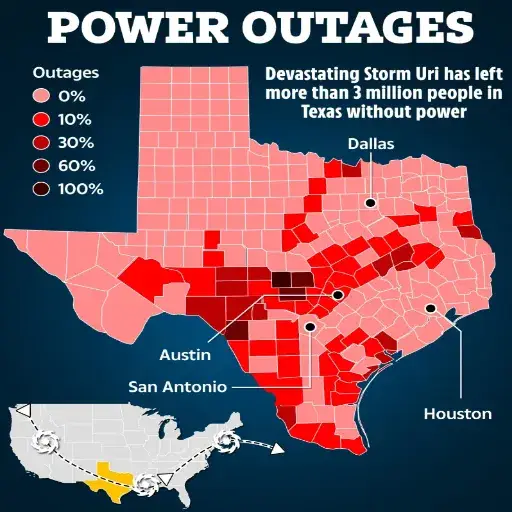
Power outages in Texas are the aftermath of extreme weather events co-occurring with high power demand and worrisome infrastructural issues in the generation path. Bad weather, such as winter storms, hurricanes, or more extreme heat, can damage power lines and equipment or simply put a strain on energy production. Furthermore, the state’s largely independent energy grid struggles to balance supply and demand during periods of peak usage. Texans should be encouraged to minimize those effects by supplying themselves with emergency kits, staying informed through reliable sources, and learning energy conservation methods in cases of critical importance.
Weather-Related Causes of Outages
Weather outages are power outages caused by extreme and unpredictable weather conditions. The very severe storms, such as thunderstorms and hurricanes, carry high-velocity winds and heavy rain capable of uprooting trees or rendering power infrastructure impotent. Ice storms and freezing rain in cold regions constitute a scenario in which ice buildup accumulates on power lines, causing them to snap from their own weight. Then come the heatwaves, which pose a separate kind of challenge by increasing the energy demand for cooling, thus leading to the overloading of power grids. Besides these, flooding serves as another significant contender, as it can damage underground systems, thereby hampering repair work by utility crews. Occurrences such as these disrupt energy supplies, underscoring the importance of having resilient energy systems that can keep pace with evolving climate patterns.
Infrastructure Challenges and Equipment Failures
With the recent updates from around the world, a handful of urgent questions or issues have arisen regarding how infrastructure can be modified to withstand more severe weather patterns. Research indicates that modernization and preventive approaches seem to be the answer. For instance, utilities are embedding new grid technologies, such as smart transformers and automated switches, into the system to identify problems before they cause large-scale failures. Secondly, older infrastructure can be made more resilient by burying power lines and reinforcing key structures. However, various other challenges lie on the path before resilience: funding issues, logistical issues, and coordination issues between government agencies and private entities. Solving these requires a multi-pronged approach based on innovation, collaboration, and proactive planning.
Other Contributing Factors to Power Outages
Another significant contributing factor is the one that has been highlighted in recent weather events due to climate change. Storms, wildfires, ice storms, and heat waves recognize the power grids as extreme rivals, leading to mass outages. Aging infrastructure is also a consideration, as many systems are outdated and thus unable to meet the increasing energy demands or withstand extreme weather conditions. Finally, with the most recent developments in digitalized control of the energy system, malicious actors have not missed a chance to exploit these vulnerabilities for good disruptive purposes. This confluence of concerns is a clarion call for urgent grid modernization to ensure communities receive a reliable energy supply. Confronting these issues requires integrative solutions that interlace capacity-dependent modern technologies, infrastructure improvements, and cybersecurity enhancements.
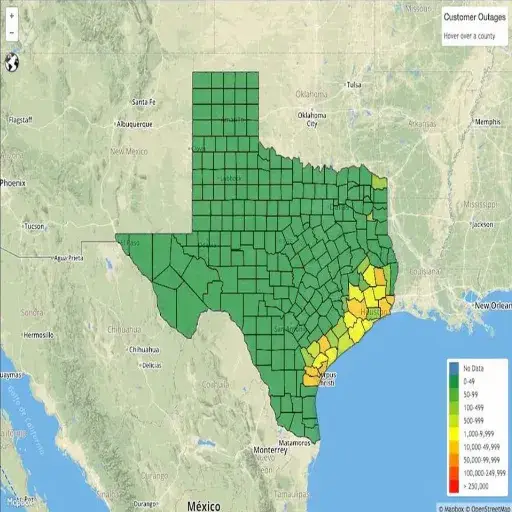
How to Use the Texas Power Outage Map
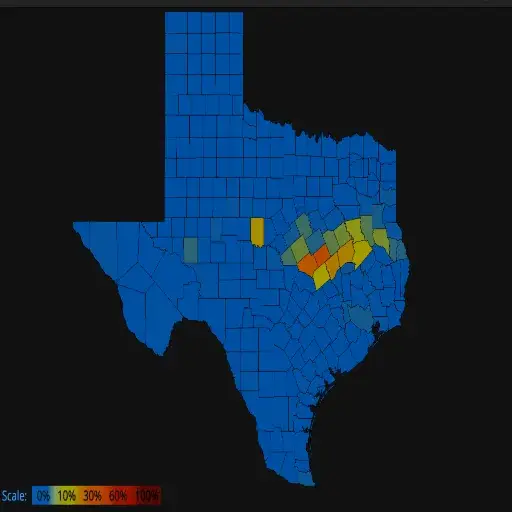
Use the Texas Power Outage Map this way:
- Access the Map: Visit the official power outage map of your electricity provider or a trusted source such as the Public Utility Commission of Texas.
- Navigate the Map: Zoom or pan to your particular region or address. Affected areas will be marked with indicators.
- Check the Legend: If in doubt, consult the legend, which explains the symbols, color codes, and their meanings, such as the number of outages or restoration status.
- View Outage Details: Click on the colored zones or symbols for more information on the affected customers, restoration time, and the cause.
- Monitor Updates: The map’s information is regularly updated in real-time. Please check back periodically for the latest updates.
Accessing the Power Outage Map
This is a guide on how to view a power outage map:
- Visit the Official Website: Head to the local energy provider’s website. Usually, providers have a section or a tool for tracking outages.
- Search for the Outage Map: Use the search bar to type in keywords such as “outage map” or “power outage information” to find the relevant page quickly.
- Enter Your Location: In most instances, the map accepts inputs such as an address or zip code to provide a more precise view of outages in their area, along with restoration updates.
- Mobile Apps & Notifications: For ease and convenience, check if your provider offers any mobile apps. The app could very well provide tracking on outages and notifications of any dates associated with their restoration.
Interpreting Key Features of the Map
Generally speaking, outage maps typically feature a few vital elements to help people determine the status of outages in their vicinity. These include color-coded zones that indicate the severity or scale of the outages, ranging from minor outages affecting a single block to extensive areas with severe disruptions. The estimated restoration time provides an approximate timeline for when services are expected to resume. Additionally, many maps display the number of customers affected by the outage in a particular area, indicating the severity of the outage.
In combination with search engine data, you can also try checking other updates or resources, such as live news feeds and social media posts, or alternative outage maps from a local authority. Therefore, you can ensure that you are getting the most accurate information regarding the issue at hand.
Common Issues When Using the Map
A typical view of the outage map is the delay of the real-time updates. With the latest data coming from search engines sometimes, there can be a disparity between outages reported and the potential outages that exist at the current stage. In response, the map should be refreshed regularly, or any updates related to this matter should be cross-checked against updates provided on official Twitter or through a local utility provider. On the other hand, users tend to associate their filtering tools, which break down an area of interest and can confuse the user about the outbreak’s actual scope. Utilizing these tools together with live data would improve accuracy and usability.
Impact of Power Outages on Residents
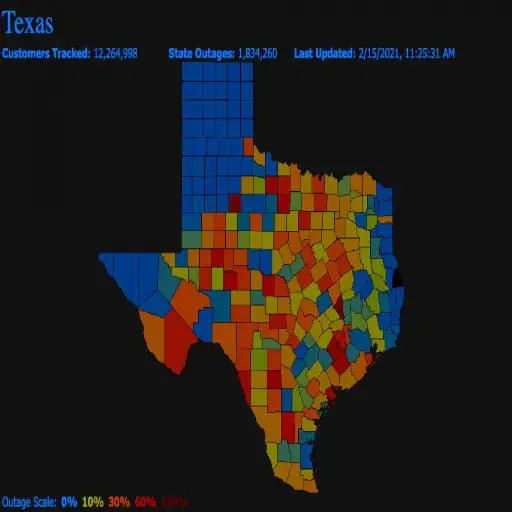
Power outages are an unwelcome interruption to a person’s daily life. They pose an inconvenience, resulting in the loss of light, heating, or cooling, from comfort to sustenance. With prolonged power disturbances, food spoilage occurs as refrigeration ceases to function, and remote work, studying, and other activities are interrupted due to limited access to essential devices and communication tools. For vulnerable individuals, such as elderly citizens or those who rely on medical equipment, outages can have serious adverse effects on their health. Outages can also induce anxiety and uncertainty, mainly when they occur during an extreme weather event or an emergency. In turn, effective and timely communication, along with regular updates, will empower residents to manage the situation effectively.
Economic Consequences of Outages
Power outages have severe economic consequences, affecting both small and large businesses, as well as individuals. For businesses, power outages imply a loss of productivity, opportunities missed for revenue, and risks of damage to equipment and inventory, especially in cases where refrigeration or a precise manufacturing process is involved. In general, small businesses are often hit the hardest since they lack sufficient resources to establish an adequate backup power system. On the other hand, outages require different kinds of expenditure. The costs might include replacing faulty goods due to power loss or powering up one’s house with a backup generator set, and in some instances, even repairs for damage caused by the lack of electricity. However, from another perspective, even longer interruptions, running into days, can weigh down on local economies as they obstruct essential services and discourage investments in new businesses. A significant investment in upgrading infrastructure for resilience and adopting the newer energy-generation vision is required to help address these economic issues arising from disruptions.
Health and Safety Risks for Vulnerable Populations
⚠️ Critical: An outage in the power supply can thus pose a significant danger to the health and safety of the populace, particularly the elderly, the disabled, and individuals with chronic medical conditions. Without a source of electricity, ventilators, oxygen concentrators, or medications under refrigeration may fail, thereby putting the person at risk of death. Heated arguments against the weather set in when the power is out: heat stroke or hypothermia can quickly become a reality for these groups. According to recent data, being equipped with backup sources of power and population support networks can significantly reduce the risk; however, most vulnerable persons may still be unable to heed the warnings or lack the necessary resources. Coordinated action must prioritize emergency preparedness and ensure equitable access to life-saving resources.
Community Challenges During Power Outages
Power outages present significant challenges that communities must address, particularly in regions with extreme weather conditions. Recent statistics indicate an increase in searches for “how to stay safe during outages” and “emergency power solutions,” further confirming widespread concern and a general lack of preparedness. These communities face particular difficulties, including limited access to heating and cooling, restricted use of medical devices, inadequate food storage, and limited communication. The most vulnerable among populations are the aged, disabled, and others at risk. To counter these challenges, one must have better infrastructure, an educated public, and programming for community resilience and preparedness.
Government Response to Power Outages
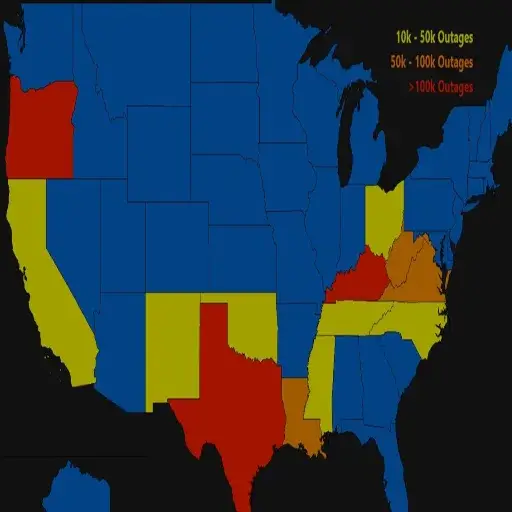
Crucial to accommodating power failures is a swift and cooperative response orchestrated by governments. Such measures include activating emergency response teams to address immediate safety and operational concerns, engaging repair crews or companies to restore power quickly, and disseminating public communications or updates to residents about the outage, its status, and available support services. Establishing emergency shelters equipped with necessities, such as heating, cooling, food, and medical supplies, is another crucial task. In the long term, efforts would focus on making infrastructure more resilient, advancing backup energy solutions, and developing concrete policies to prevent future disruptions.
Recent Actions by Texas Authorities
The Texas authorities have been working to resolve infrastructure challenges and ensure energy reliability all over the state. Among the recent actions taken in the state is a massive investment in the modernization of the electrical grid, aimed at withstanding extreme weather conditions. Other interventions that are given emphasis include mandating the winterization of power plants and enhancing energy storage capabilities to prevent outages during times of critical demand. The authorities further issued incentive programs to encourage the adoption of solar and wind energy, aiming to diversify the energy portfolio. Public awareness campaigns have also been launched to educate residents about conservation measures and emergency preparedness. It is to this end that these activities aim to develop a more resilient and sustainable energy system for use by Texas residents.
Debates on Energy Policy and Infrastructure
One of the significant issues of energy policy and infrastructure has been the trade-off between sustainability and reliability. Conservationists maintain that solar, wind, and other clean energy systems remain a vital means of combating climate change and reducing dependence on finite fossil fuels. The opposite maintains that even today, it may not be possible for renewables to provide dependable power at the time of demand, ie, during peak periods or extreme weather events. This stirred discussions on the use of natural gas and nuclear power as potential “bridge” options to stabilize the grid while advances in renewable technologies and storage capabilities are made. This intricate decision confronts policymakers with what to prioritize in investments, what to incentivize, and how quickly to accelerate the energy transition, all to assemble a cohesive system that effectively addresses both short-term and long-term energy challenges.
Emergency Measures and Relief Programs
Emergency measures and relief programs play a crucial role in mitigating energy crises that disproportionately affect vulnerable groups and essential infrastructure. Governments and organizations establish financial assistance programs to alleviate the burden on households facing rising energy prices through subsidies or temporary price caps. Relief programs subsidize vital services such as hospitals, schools, and transportation to keep them operational during an energy crisis. Then, at an international level, collaborations and strategic reserves are utilized to stabilize the energy supply, while the advancement of forecast modeling enables governments to better prepare for potential disruptions. The efficiency of these measures is aimed at addressing urgent needs while simultaneously developing resilience in energy systems.
Preventive Measures for Future Outages
Some key measures could be taken to exploit opportunities to preclude any possible future energy outage:
🌱 Investing in Renewable Energy
If resources are spent on tapping solar, wind, and other renewable sources, it reduces dependency on fragile and limited supply chains.
🔧 Modernizing Infrastructure
Refurbishing and upgrading power grids and storage facilities will enhance reliability and provide increased capacity to accommodate fluctuations.
💡 Implementing Energy Efficiency Programs
In principle, energy conservation is encouraged through technology interventions, and intelligent systems are in place to ensure demand is offset.
🔗 Developing Decentralized Energy Systems
Microgrids and distributed energy production can significantly enhance system resiliency by reducing reliance on centralized arrangements.
🛡️ Enhancing Cybersecurity
Securing energy systems against cyber attacks will eliminate disruptions caused by malpractice.
Infrastructure Upgrades and Renewable Energy
Upgrading infrastructure in conjunction with the development of improved renewable energy sources is crucial if climate leaders aim to mitigate climate change and achieve long-term energy independence. Recently, renewable energy has continued to become increasingly efficient, with solar panels and wind turbines becoming ever more affordable and accessible. By upgrading the energy grid to enable the integration of distributed energy resources, innovative grid technologies, and battery storage systems, utilities can ensure high reliability and flexibility. When modern infrastructure and clean energy are viewed as investments, societies can reduce carbon emissions while meeting rising energy demands sustainably.
Community Preparedness Tips
Preparedness is crucial to building resilience within communities facing disasters or emergencies. Here are a few essential things to consider:
- 📞 Develop a Communication Plan: Ensure that everyone in your community or household knows how to reach one another and where to meet in case of separation. Provide a local emergency contact and one that is out of the area.
- 🎒 Build an Emergency Kit: Pack water, non-perishable food, flashlights, extra batteries, a first-aid kit, essential medications, and important documents. Having supplies should cover for as many hours as at least 72.
- 📱 Stay Informed: Pay special attention to local weather alerts, any breaking news, and announcements from the local community. If available, consider downloading apps and signing up for local alert systems.
- 🔄 Conduct Regular Drills: Organize evacuation and other safety procedures for your family or the community to ensure everyone is prepared. Knowing how to respond during fires, earthquakes, or severe storms can be a lifesaver.
- 🎓 Engage in Community Training: Attend local programs or workshops on first aid, CPR, or disaster response to enhance your skills and knowledge. Cities most often encourage community preparedness through these resources.
- 👥 Plan for Vulnerable Groups: Consider children, elderly persons, and pets when making your plans and preparing your emergency kits. Everyone must be accommodated.
Policy Recommendations for Energy Resilience
Enhancing energy resilience requires the highest priority to be given to investments in renewable energy technologies, including solar and wind power, which reduce reliance on centralized grids. Community microgrids and battery storage on the distributed level for local use should be encouraged to provide power during emergencies. Additionally, introducing new infrastructure while incorporating innovative grid technologies will yield greater efficiency and flexibility. Energy efficiency can be promoted to a level that supports resilience in the face of disruptions. Also, residents should be encouraged to conserve energy.
Reference Sources
There are five top-notch sources at the professional and authoritative level that you can regard for ensuring the accuracy of the article, namely the “Texas Power Outage Map.”
| Source | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| PowerOutage.us | This website would display real-time data on power outages across Texas, including the number of customers affected and updates from electric providers. | |
| AEP Texas Outage Map | It is possible to look up detailed accounts of power outages on a timely and reliable basis, particularly in AEP Texas’s service areas. | |
| The 2021 Texas Power Crisis Study | The study aims to conduct a thorough analysis of the 2021 power failure in Texas, which clearly revealed the vulnerability of the State’s energy infrastructure and highlighted the need for improvements and positive developments. | |
| ERCOT Blackout 2021 – UT Energy Institute | The outcome will provide students with exposure to real-life industry problems while they learn vital lessons from the blackout itself. | |
| Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) | ERCOT is the primary organization responsible for managing Texas’s electric grid. Its website provides official data, reports, and updates on grid performance and outages. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Texas power outage map?
A Texas power outage map is a visual representation that shows the current status of electrical service across different regions in Texas. It highlights areas experiencing outages, allowing residents to stay informed about power disruptions in their neighborhoods.
How can I see the power outages in Texas?
You can view power outages in Texas by visiting the websites of utility providers that offer interactive outage maps. These maps display real-time information on outages, including estimated restoration times and affected areas.
Who provides the Texas power outage map?
Local utility companies, such as Oncor and CenterPoint Energy, among others, typically provide the Texas power outage map. These providers maintain the maps to inform customers about service interruptions and restoration efforts.
How often is the Texas power outage map updated?
The Texas power outage map is generally updated in real-time or every few minutes, depending on the utility provider. This ensures that residents have access to the most current information regarding outages and service status.
What should I do if I see a power outage on the map?
If you see a power outage on the map, report it to your utility provider if it hasn’t already been reported. Additionally, you may want to prepare for potential extended outages by gathering essential supplies, such as water, food, and extra batteries.
How do I find my power provider in Texas?
You can find your power provider in Texas by checking your electricity bill or searching online with your address. Various websites also offer tools to help you identify your provider based on your location.
Are there resources available for tracking power outages in Texas?
Yes, several resources are available for tracking power outages in Texas. Utility companies offer online maps, mobile apps, and customer service hotlines that enable residents to check the status of outages and track the progress of restoration efforts.
What causes power outages in Texas?
Power outages in Texas can be caused by a variety of factors, including severe weather events like storms or hurricanes, equipment failures, and increased demand on the power grid. Understanding these causes can help residents prepare for potential outages.
Can I receive alerts about power outages in Texas?
Many utility providers in Texas offer alert systems that notify customers about outages in their area. You can sign up for these alerts via text, email, or phone call to stay informed about any service interruptions.
