In the realization of the generators, one of the most important dilemmas is to decide whether to use single-phase or three-phase generators. This choice affects in a very important way the power requirement, efficiency, and general capability for various applications from residential to industrial settings. However, what differentiates these two types, and most importantly, what do we base the decision on in our selection of the perfect one to suit our needs? In this guide we hope to explain the technical aspects of three-phase and single-phase generators so that you know the differences, pros, and ideal cases for their use. If you are going to power a machine, a piece of construction equipment, or any household appliances, the reason why you should know these is so that you can wisely put your dollar in your choice of generator. Here, let’s consider the key differentiating features of these generator types to help you make a decision on which of them best fits your needs.
Introduction to Three Phase Generators
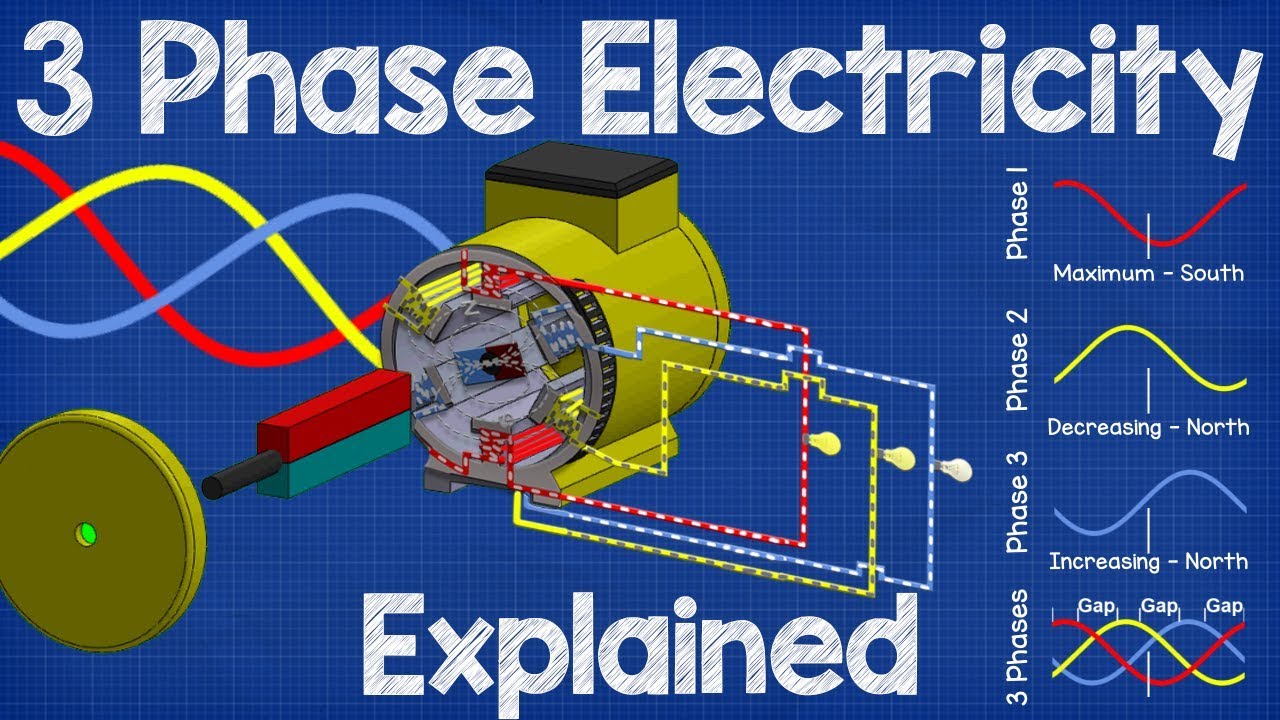
Definition and Overview of Generators
Generators are systems designed to transform mechanical energy into electrical energy through the principle of electromagnetic induction—a critical transformation required for power generation in homes, industries, and businesses. In a generator, the magnetic field moves, inducing an electric current in a conductor (a coil of wire) through this magnetic field. Generators do not produce energy; instead, they convert energy from one form to another, making them one of the pillars of modern energy systems.
Three-phase generators are a form of AC where three coils or windings serve as three-phase outputs. These windings are arranged at specific intervals to produce three-phase voltages separated by 120 degrees in an ideal manner. This arrangement ensures the power generated is distinctly balanced, which is essential for units that habitually bear a heavy electrical burden. The top-rated efficiency, reliability, and low power losses are responsible for the adoption of three-phase systems in power generation and electricity distribution, obliterating other systems on a global scale.
Key Insight:
Generators are used in applications covering extremes—from portable backup provision to large turbines within power plants. In electrical grids, manufacturing, and other high-demand environments, three-phase units are preferred due to their capacity to deliver power stably over enormous distances.
Importance of Three-Phase Power
Three-phase power makes guaranteed flow of electricity possible—consistent delivery is the reason behind its prevalence in heavy-duty electric systems. Unlike single-phase connections with irregular delivery, three-phase connections ensure a smooth supply of power. Consistent power is essential for heavy machinery, large motors, and equipment that requires substantial power to perform effectively.
Energy transmission efficiency is another critical advantage. For practical reasons of minimizing energy loss, three-phase systems make an attractive low-cost option for power delivery in cities, factories, and other high-usage environments. This type of power uses less conductor material for the same amount of power, thus saving infrastructure costs while being more efficient in transmitting considerable amounts of electricity.
- Accommodates renewable energy sectors such as wind farms and solar installations
- Compatible with sustainable energy solutions
- Promotes cleaner and efficient technology for future electrical consumption
- Delivers reliability, efficiency, and adaptability across energy systems
Comparison with Single-Phase Generators
Three-phase generators are most efficient, robust, compact, and cost-effective in meeting high-power requirements, while single-phase generators are simpler, cheaper, and best used for low-power needs.
| Key Point | Three-Phase | Single-Phase |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High | Low |
| Durability | More durable | Less durable |
| Compactness | More compact | Less compact |
| Cost | Higher upfront | Lower upfront |
| Power Output | High | Low |
| Applications | Industrial/Commercial | Residential/Small-scale |
| Energy Waste | Reduced | Higher |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| RPM | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | More complex | Simpler |
How Three Phase Generators Work

Basic Principles of Three-Phase Current
An important concept in electrical engineering is three-phase current, which works by sending three alternating currents at the same frequency and amplitude, with each phase 120 degrees out of phase. With these settings, it becomes reasonable for smooth and consistent power movement in a balanced system, explaining its wide use in industrial and commercial systems. Whereas flux of AC power is followed in single-phase systems, three-phase systems provide constant power transfer, thus ensuring excellent efficiency and stability for heavy machinery and high power requirements.
The crux of the system lies in the generating unit—typically a three-phase generator made up of a rotor carrying a magnetic field and stator armature windings arranged in three locations spaced equidistantly from one another. As the field rotates, it creates currents in the three windings, shifted by 120 degrees, which then lead to the generation of distinct phase levels. This arrangement helps reduce energy wastage and ensures the system moves much smoother while keeping undue stresses off the conductors by sharing the workload among all three phases.
Technical Advantage:
Three-phase systems carry greater power density than single-phase systems and are capable of supporting both high-voltage transmission and low-voltage applications. They are the primary power supply for industrial machinery, motors, and large-scale heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Components of a Three-Phase Generator
A three-phase generator is made up of numerous key components that cooperate to yield reliable and efficient electric power:
Stator
The stationary component where electric energy is produced with the help of windings. Three coil pieces are arranged 120 degrees apart to produce electricity of the three phases.
Rotor
The rotating component normally connected to a mechanical prime mover (such as a turbine or engine). It produces the magnetic field to induce current in the stator windings.
Prime Mover
An external mechanical source that drives the rotor, including diesel engines, gas turbines, or water turbines in hydroelectric plants.
Exciter
The source of the initial magnetic field needed to start the initiation process. Modern systems often use brushless exciters for long-term maintenance.
Voltage Regulator
Adjusts the field winding to maintain the desired voltage level, ensuring no fluctuation in power delivery even when the load changes.
Cooling System
Heat generated during operation necessitates an efficient cooling system, either through air or liquid cooling, to maintain safe temperature range and extend machine life.
Control Panel
The place where monitoring and operational control come together. Displays parameters such as voltage, current, and frequency with built-in protective functions like overloading and emergency stops.
Operating Mechanism and Power Output
The three-phase generator mechanism works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Fundamentally, the rotor of the generator is turned by an external power source—such as diesel, solar, wind, or a turbine—inside a static magnetic field. The movement of these parts creates electromotive force in the stator windings, which are connected around the rotor with several conductor windings. Keeping the magnetic field cyclically fluctuating when rotating ensures the output current flows alternately. The efficient operations of this system in generating power negate the necessity for a neutral line in this autonomous three-phase system.
Three-phase generators are known for their high efficiency and adaptability to a wide range of applications. The power output of a generator depends mostly on the construction of the rotor and stator, the speed of rotation, and the intensity of the magnetic field. Modern generators are manufactured with advanced materials and refined engineering, aiming to cut down on energy losses and produce more power in the process.
Modern Technological Advances
- Superconducting Materials: High-efficiency models use these materials to minimize resistance and excess heat creation
- Speed Control Mechanisms: Enable generators to run at optimal speed, ensuring constant power under varying load conditions
- Real-time Monitoring: Controllers and sensors allow operators to monitor voltage stability, load distribution, and fuel efficiency
- Predictive Maintenance: Reduces sudden breakdowns and expensive repairs through advanced monitoring systems
Advantages of Three Phase Generators

Power Density and Efficiency
Higher Power Performance
Compared with single-phase generators, three-phase generators provide power more efficiently and compactly with greater power density, size for size and weight for weight.
Balanced Load Distribution
Three-phase generators balance load distribution much better, reducing maintenance cost due to wear and tear, and improving overall performance.
Energy Efficiency
Reducing losses through lower conductor material requirements ensures higher energy efficiency over time.
Uninterrupted Power Supply
Three-phase generators generate power without voltage fluctuations, ensuring uninterrupted power supply for connected devices and systems.
Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
By being efficient and resistant, three-phase generators are low-cost in terms of operations and maintenance, making them a cost-effective decision for businesses.
Load Balancing and Stability
- Balanced Sharing of Loadings: The three-phase procedure ensures electrical loads are proportionally distributed across the three phases, offering a lesser chance of uneven loading and boosting overall system efficiency.
- Enhancing System Steadiness: With well-balanced current in all three phases, oddities in voltage changes are minimized, preventing collapse of electrical supply to apparatus and improving their service lifespan.
- Elimination of Neutral Current: With energy users ideally balanced, there is almost insignificant neutral current in three-phase systems, increasing operational efficiency while decreasing energy loss.
- Component Robustness in Failure Situations: Because of its balanced nature, a three-phase system might continue functioning despite failure in one phase, assuring no power stoppage in critical conditions.
- Better Power Factor: Distribution transformers support phase-to-phase power factors as opposed to phase-neutral power factors, reducing absorbed energy system costs.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Three-phase electrical systems operate better than almost any electrical system in industrial applications because of their higher efficiency, dependability, and extensibility. Here are their operation and advantages in industrial settings:
High Power Capacity
Three-phase systems have enough power to operate large machinery and manufacturing equipment. A typical three-phase system can deliver 1.732 times the amount of power that a single-phase system can deliver with the same current and voltage.
Efficient Transmission of Energy
Due to balanced transmission lines, energy losses in three-phase systems are much lesser when maintained over distance. Industrial setups have transference losses of about 15-20% less when compared with single-phase transmissions.
Less Maintenance
Studies note that equipment or machines driven by three-phase power will stand longer, with lifespan extended by an additional 50% compared to equipment driven by single-phase systems.
Scalability in Power Distribution
Three-phase systems are very useful in scaling up industrial operations. They can sustain operation on a wide range of voltages, catering to power needs from smaller facilities to huge complexes without major alterations to infrastructure.
High System Reliability
Balanced loading of the three phases minimizes the extent of interruptions in supply. The system operates in a non-impaired manner even if one phase has difficulties. This is of ultimate importance for industries such as manufacturing and data centers that need high uptime.
Common Applications of Three Phase Generators

Industrial and Commercial Uses
Labeled as the most preferred in the industrial and commercial sectors, three-phase generators serve to accommodate high-power applications efficiently. They are commonly installed within manufacturing plants where they operate large machinery systems including conveyor systems, robotic arms, and industrial motors. Practical applications also include construction worksites for using cranes, welders, and compressors.
The demand for hospitals, information technology installations, and large office buildings has made these generators basically indispensable for robust and backup power. Used in hospitals to keep life-saving equipment running during power outages, and in data centers due to their high reliability, these generators are crucial to avoid downtime that would result in substantial financial losses. One application worth mentioning occurs in retail complexes and hotels with multiple buildings, where heavy HVAC loads, elevators, and lighting must be addressed efficiently.
Key Industrial & Commercial Applications
- Manufacturing plants
- Construction sites
- Healthcare facilities
- Data centers
- Large office buildings
- Retail complexes
- Hotels
- Renewable energy projects
Generators are additionally essential components in renewable energy projects, serving various applications in large-scale wind turbines and solar farms. The motor’s adaptability in several applications identifies it as a crucial component in use across many domains.
Specific Applications in Diesel and ATS Systems
Diesel generators are widely used as primary or backup power sources in parallel with Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) systems to ensure continuous electric supply during an outage. Once a power failure occurs, the ATS systems instantly detect the power loss and activate the running diesel generator, thus ensuring that systems continue to function with minimal impairments.
Critical ATS Applications
Healthcare Sector: Hospitals rely on these ATS systems and diesel generators to keep life-saving equipment and emergency services intact even during grid outages.
Industrial Setups: Data centers deploy these systems to protect critical processes and data. Diesel generators with ATS technology keep production lines functioning and servers continuously running, preventing financial and operational risks.
Advanced Features: Enhanced technological features of ATS systems such as remote control and smart grid interconnection offer accuracy and efficiency, in agreement with the needs of contemporary infrastructure and energy management systems.
Benefits in High-Power Circuits
In configuring the establishment of heavy industrial frameworks where accomplishment of energy transmission on a large scale is employed, high-power circuits are closely knit. These circuits can be instrumental in achieving enhancements concerning energy saving, higher efficiency, reliability, safety, and scalability.
| Benefit Category | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Transmission Efficiency | High-quality regulated circuits minimize energy loss during transmission. By stepping up voltage in power grids, losses can be significantly reduced. | ~70% reduction |
| Reliability | Generate constant power supplies with minimized breakdowns, averting critical application disruptions. | Fewer blackouts |
| Security Features | Support protective devices like circuit breakers and relays to provide operational safety against overloads, short circuits, or surges. | ~60% risk reduction |
| Scalability | Developed to withstand increases in load levels without jeopardizing performance, essential for renewable energy industries. | High adaptability |
| Modern Technology Compatibility | Completely integrated into automation systems and smart grids for precise energy measurement and system efficiency. | ~30% efficiency gain |
Maintenance Tips for Three Phase Generators

Routine Maintenance Practices
Precautionary maintenance carried out on three-phase generators is necessary to guarantee machinery reliability while avoiding major breakdowns which could prove expensive. Such maintenance types involve scrutinizing the generator for visible signs of wear, like frayed cables, loose electrical connections, or physically damaged parts.
Essential Maintenance Checklist
- Oil Level Monitoring: Regular checking and replacement according to manufacturer’s requirements guarantees optimal performance
- Filter Maintenance: Supplying clean filters affords heat control and avoids heat-induced blockage that could hamper operations
- Visual Inspections: Check for frayed cables, loose connections, or physical damage
- Load Testing: Determine if the generator can handle designed capacity without issues
- Voltage Regulation Tests: Ensure proper voltage output across all phases
- Frequency Checking: Verify stable frequency output
- Software Updates: Update control-system software when applicable
Load testing features as a crucial point of daily maintenance. These tests determine if the generator can handle the designed capacity without any issues. Different speeds can be evaluated during the test to reveal possible performance bottlenecks. When encountered, technicians can solve any issues prior to escalating them.
Storage and Environmental Protection
Proper Ventilation: Store in well-ventilated areas to avoid moisture buildup that may result in rust or electrical issues
Dry Environment: Keep generators in dry locations to prevent corrosion and electrical problems
Fuel Quality: Clean tanks regularly to prevent contaminant/sediment build-up and maintain fuel quality
Best Practices for Longevity and Performance
In order to make your three-phase generator last as long as possible and perform to the hilt, frequent check-ups and rigorous maintenance are necessary. Here are the best practices to follow:
Component Inspection
Arrange scheduled checks of mechanical components like belts, bearings, and power connections. Worn or broken parts impair total efficiency, so replace defective components immediately to prevent larger damages.
Fluid Level Management
Monitor fluid levels of cooling, lubricants, and fuels constantly. Uncontrolled levels lead to overheating, excessive wear, or even catastrophic failure.
Proper Ventilation
Generators generate heat under operation. Without proper airflow, overheating may occur, leading to decreased efficiency and functional failure. Place generators where air can circulate freely with no obstruction.
Load Management
Load the generator within safe operating capacity. Overloading causes stressed operation issues, while underloading leads to carbon buildup over time, affecting performance.
Professional Testing
Load bank tests simulate real-world operating conditions and ascertain that generators can withstand the relevant output. Have qualified technicians inspect electrical connections, wiring, and control systems.
Advanced Monitoring
Newer generators come with sophisticated diagnostics tools or gauge-combines. Regular data monitoring systems can show the inception of issues before they become serious problems.
References
-
EE 303 Energy Systems and Power Electronics Three-Phase Systems
This document from Iowa State University explains the working principles of three-phase generators, including their structure and voltage production. -
Lesson 13B: Three-Phase Power
Published by the University of Louisville, this resource details the configuration and operation of three-phase generators, including coil placement and magnetic fields. -
How Power Grids Work
From Smith College, this source provides insights into the role of three-phase generators in commercial power grids and their operational advantages. -
ECE 3600 3-Phase Power Notes
A resource from the University of Utah, discussing the benefits of three-phase power for motors and generators, especially for high-power applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a three-phase generator and how does it differ from a single-phase power source?
A three-phase generator consists of three separate winding sets, each phase generating an alternating current 120° out of phase with the others. The three-phase power that results provides smoother delivery of power currents to loads as well as constant torque when compared to single-phase power. More power can be carried over three wires (or four wires with neutral) when the three-phase system operates. It proves beneficial for large motors and industrial appliances.
Why do large motors and pumps run on three-phase generators instead of single phase?
Comparable to single-phase supply, three-phase motors satisfy the need for a short starting period and higher starting torque through a “rotating magnetic field” at breakaway in the motor. This motor has a constant-torque characteristic and an absence of severe throbbing or oscillating effects in the initial stage, which is liable to damage motors with insulated failure. Three-phase generators are suited to applications in agriculture and related industries where high starting currents and reliability are given preference.
How is it possible for a three phase generator to produce more power compared to a single-phase generator?
Three-phase generators exhibit more efficient power production for similar apparent power ratings. For a load rating in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (hp), a three-phase generator can deliver more power through the system over less conductor than through a single-phase or split-phase system. In real-life administration, a 480 volt three-phase generator unit can support heavy loads and bulky motors from three-phase power supply lines with minimal phase power distribution and phase imbalance.
What are the customary wire voltages and phase wiring for a three-phase generator?
Commonly known arrangements are either three wires for a balanced three-phase load or four wires when neutral is required. Generator systems can have different voltages depending on regions. 480 volts three-phase systems are standard in industrial situations. Maintaining correct grounds and adhering to compliance issues ensure safety and deter current flow along unintended pathways.
How does three phase generator affect issues related to electronics and emissions?
Three-phase power is great for motors and heavy loads, but electronics and sensitive appliances could require conditioning or conversion into single-phase or DC. Generators can discharge biblical and directional harmonics. In industrial applications, generated harmonics are required to comply with regulations. Using filters, neutral grounding, and inverters keeps interference to the barest minimum and eliminates direct radiation onto the tri-phase bleed.
Can a three phase generator be used for standby power or for household appliances?
Generators provide standby power to commercial sites while also maintaining homes when adapted correctly. Many households use split-phase derived from a three-phase source or single phase taps for appliances. If you only plan to meet basic home or small business electrical requirements, a single-phase 2-wire supply delivered by the three-phase inverter or three-phase generator would suffice.
What could make a three-phase generator face an imbalance? What are the consequences?
Uneven loads cause peaks and valleys in phase power and create circulation currents in the three phases. This could lead to overheating of generators and motors, increased vibration, and decreased efficiency. Proper load distribution—monitoring and possibly leading to power factor correction—seems to be the greatest method of decreasing the imbalance. This makes the current flow into houses and not into unwanted components.
How can a three-phase generator produce a rotating magnetic field and why is this essential?
The stator windings in the generator produce three alternating currents that are shifted by 120 degrees, producing a rotating magnetic field that rotates the motor yet generates stable torque while interacting with the rotor. This rotating field is primary in order to make the drive for electric motors smooth, avoid any pulsate torque existing with single-phase systems, and provide high torque for starting to move heavy loads of the required equipment.
Key Takeaways
Superior Efficiency
Three-phase generators provide higher power density and efficiency compared to single-phase systems
Balanced Operation
Load balancing across three phases ensures stable, uninterrupted power supply
Cost-Effective
Lower maintenance costs and extended equipment lifespan deliver long-term savings
Versatile Applications
Suitable for industrial, commercial, and renewable energy applications
