Unexpected power outages can be a real headache, and a good quality generator is what you need to keep your business premises or home afloat. However, it’s not easy choosing the correct generator among the many available on the market. Should a portable generator be chosen for convenience and adaptability or a standby generator for guaranteed power backup? This article seeks to help analyze and understand the importance of portable and standby generators to make your preferred choice clear in relevance to your needs. Proceed with reading to understand specific aspects, advantages, as well as some differences between the two energy alternatives to keep you always ready for whatever may come your way.
The Basics of Generators
A generator is simply a machine that produces electric power in the absence of a power supply or when the supply cannot be connected. A portable generator, as the name suggests, is lightweight and easy to carry, making it perfect for use as a temporary power source, especially during camping, tournaments, or even a crisis. Stationary Generators are installed as a permanent feature and come on automatically when there is a power cut, thus making them the best for long periods, for instance, in a house or business which cannot afford a power cut for long periods. The decision depends on what you need, that is, mobility, amount of power, or the cost.
What is a Portable Generator?
Noise pollution caused by stationary generators is much less pronounced because the overwhelming majority of units are small, portable devices. A portable generator is a very small device designed to supply electricity temporarily during power cuts or in remote areas to provide access to electricity. Such generators use engines that run on gasoline, diesel, or propane and produce power by rotating an alternator that changes mechanical energy into electrical energy. These portable generators come in various sizes and capacities, ranging from household versions that can only power several devices to heavier-duty machines that come in unit with construction tools.
Typically, modern portable generators come with many such as several outlets and even a USB port, along with cutters for the sake of preserving appliances or anyone. Most wattages as regards these generators range in 2000 watts to 7500 watts. This depends basically on the size. Take, for instance, a 3kW generator would be able to operate a fridge, some lights, and a blow fan but those heavier than average 5kW would be used with bigger appliances like air conditioners or heaters.
In addition to this, even small portable Generators come with technology that helps to maintain the quality of the supply, similar to what is needed for laptops and mobile phones. Its capability to be moved is increased by its light weight, and there are wheels and handles for the tool such that they can be used for different occasions, such as parties, camping or even house backup during power outages. More recently, energy efficiency and quiet operation have significantly enhanced the user – user-friendliness of portable generators, which are a necessity for many applications.
What is a Standby Generator?
Stationary Generators operate as a failsafe for a specific system of the house or office to back up electric supplies in the event of blackouts. In comparison to portable generators, stationary generators are located outside the facility as well as directly connected to the electric installations. It is powered by an auto switch that will indicate the absence of an electric supply and make the unit operational within no time.
Stationary generators run primarily on gas and propane, both of which can be delivered through an existing utility line or a storage facility, thus eliminating the need to go to every machine and refill it one after the other. Sometimes the generators come in different sizes, depending on the application – there are small ones used in households and such that rely on the necessities of some devices in a particular house; and there are big ones used in businesses to provide support for such establishments by powering up the entire building.
As per the trade wisdom, many standard home stationary generators would have a power output of 7kW up to 24kW, while big industrial generators would go beyond 150kW power, due to the vast requirements. Especially with the latest developments, such as quieter running, mobile monitoring, and enhanced efficiency, these have become more efficient and user-optimized. These types of gensets are very useful in augmenting uninterrupted electrical power backups in hard-to-reach areas, especially in emergencies arise as a result of hurricanes or consistent power cuts.
Key Differences Between Portable and Standby Generators
Small power stations are divided into portable and stationary generators used for different conditions and purposes. Portable machines are often small and require assembly and connection before they can be used. Such machines are run on fuel like gasoline and diesel and produce between 1kw to about 12kw of power. The uses of such generators are many, including family outdoor functions and camping, or even in homes for a limited time when there is no power. Most portable generators are easy to use but noisy and need regular filling of fuel tanks, unlike the standby generators.
Next, there are the stationary generators that are based in one area, and once installed, they do not require any activation; their on-off action is automatic. They are hooked to the electrical grid of the house or the business, and gas or propane is used to run them. Sizing from an average of 7kw to over 150kw on commercial units, they are geared for comfortable and efficient long-term use. Besides, unlike the portable ones, they are automatic and hence in case of power failure, there is no procedure to do to turn them on. Moreover, they even come with such useful features as noise suppression and remote monitoring, thus adding to the comfort of use.
The other main difference that distinguishes such generators is the price and the associated maintenance. In the case of portable generators, the prefactory costs are lower and span from $300 to $1,200 for the entire finished product, depending on wattage and functionalities. On the contrary, in the case of standby generators, the cost of installation is high, ranging from $7,000 to $20,000. Nevertheless, the benefits remain over time as these require minimal efforts in operation and are very reliable. Since each of the portable and standby types of generators offers its own benefits, the decision is based on the power needs, available finances, and the period of use.
Functionality of Generators
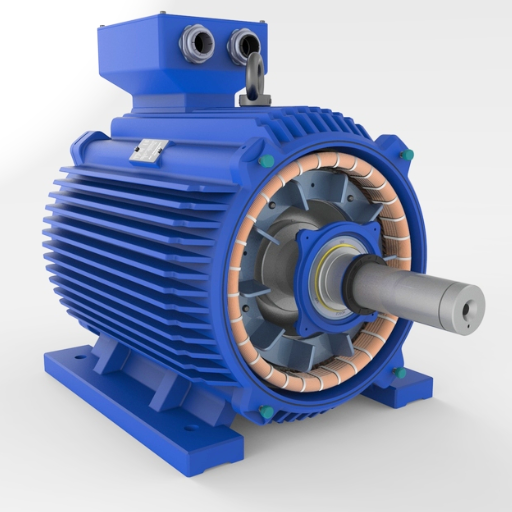

The devices called generators essentially work by the process of converting the motion into electrical energy and providing, in case of the mains power being cut off, or where there is no connection to the grid. This feature is enabled by the presence of one other major component, a machine that operates by internal combustion. However, the fuel might not always be gasoline and could be other hydrocarbons, such as diesel or gas called propane. In particular, it is used solely to drive an’ another machine called an alternator. The electricity produced by the alternator is subsequently used to provide power to various equipment, functions, or devices. For quick power applications, portable generators are preferred over other types of generators because they are compact, hence easily transferable; whereas, standby generators are fixed and turn on by themselves in case of power failure, providing a more reliable and stable form of power.
Power Generation Process in Portable Generators
A typical small generator operates by transforming the mechanical energy into electrical energy with very simple mechanism. The fuel-sparked engine provides mechanical energy to the attached generator. The current is induced within the wires in the alternator by the interaction of the magnetic fields enclosing the wires. In addition, modern portable generators contain several advancements to optimize effectiveness and utility. On the other hand, sinusoidal inverter generators work on the principle of conversion of the electrical energy produced in a sine wave form by advanced electronics, and can easily be used in marvelous devices such as mobile phones and computers. Power rating or the load the generator is supposed to carry is determined by the type and the amount of rest room per kilowatt and in mobile generators, this starts with a few watts to an approximate maximum of 10,000 and at times even much more watts. New developments, such as economics or fuel-saving modes and carbon monoxide sensors, have also been incorporated in the latest versions for users to have safe and inexpensive operation of the machines.
How Standby Generators Generate Power
Standby generators are made to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy. Internally, there is a combustion gasoline engine that is also coupled with a generator alternator. Often, people use these generators whenever there is a power cut. After all, that is why these devices were made. Once the utility power goes off, the generator knows and turns on automatically. In most cases, the power is restored in a few seconds, before the vital equipment, or lots of household and commercial appliances, begin to be powered by the generator.
Stationary generators are usually equipped with an Internal Combustion Engine or ICE, similar to refrigerants, gas compressors, or diesel engines. The highlights of their operation are based on the Principle of Oersted Conductor, the charged conductor, i. e. rotor assembly, assists resolution of the magnetic field by electromagnetism. And In factories, alternators are used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, which in turn provides power for domestic or industrial use.
Modern standby generators come in different outputs. The most common standby generators used in homes have a power range between 7000 – 20000 watts. However, a large commercial standby generator is capable of producing even more than 150,000 watts. Most of the modern generator models also have many state-of-the-art features. Some come with load management, whereby unnecessary loads are reduced or eliminated to provide power to critical requirements. The design of some models is such that they are much quieter than the previous models. Some models also incorporate smart monitoring systems, which allow the user to view and control the performance of the generator from a phone or a website. Such features help in ensuring that the user will have enough power, will be energy efficient and the power will be easy to generate, in case of an emergency.
Portable Generator and Stationary Generator Comparison of Power Delivery
In comparing the two common types of generators, portable and stationary, as regards the power delivery, one must consider the parameters such as volume, running time and how efficient they are.
Mostly, the portable generators have an output that ranges from 1,000-10,000 watts, which is comfortable to use for basic home appliances and multiple working tools when there is a power blackout or any other outdoor function. These types of generators are built in a way that makes them easy to transport, as most of them are mounted on wheels or come with a handle. However, they have smaller tanks, which limit the time that they can run to between 8 and 12 hours only when not fully loaded. They best fit in short energy supply requirements, where there would be a necessity for an alternative source of energy, e.g. on a building site, a campsite etc.
On the contrary, fixed or standby type Stationary Generators produce high power of around 7,000 watts to 50,000 watts and higher. The equipment is permanently attached to a building or a facility and is connected to the electrical supply of the building, providing power automatically in the case of a power failure. These systems are capable of using propane or gas fuel and hence have a long operation without the intervention of refilling tanks with any kind of fuel. Existing home or infrastructure facilities do not have issues of long black out periods, especially for such Houses, Firms, or Buildings.
Although portable generators provide little power compared to stationary ones and are cheap and easy to acquire, stationary models offer more power and are more practical by allowing their users to use them for such purposes. The selection of an appropriate variant is based on the requirements, affordability, and the extent of power provision sought.
What are the Applicable Environments for Different Generators?

Generators in the form of a box are best used in situations that are temporary or involve movement, such as picnics, outside parties, construction work and when all the power is dead. On occasions of going camping or in case the power goes out a designator in the form of a box may also be used.
Stationary Generators, on the other hand, are more effective in long-term and essential functions like houses, hospitals, or a company. Such generators are used to address disruptions in power supply and are often installed automatically to maintain certain critical systems in, without limitation, heating and ventilation systems, medical devices or cooling.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Portable Generators
Advantages of Portable Generators
- Mobility: Their designs make them portable and convenient to use for outdoor activities or in emergencies, which means that they are light and easy to carry around.
- Cost-effectiveness: These generators are considered less expensive in comparison with stationary generators since many people find them useful as they are pretty cheap.
- Convenience: In most cases, these generators are quite simple to operate, and do not require much needful for assembling; others even have a pull cord or a button for easy starting.
- Multipurpose: These generators are very useful when it comes to camping, tailgating, using tools at job places where there is no electricity, and even during circumstances when the power is out.
- Fuel Compatibility: Many portable generators work on gas, propane, diesel or a two-fuel alternative system, which is advantageous in the case of different conditions.
- Mechanically Inexpensive: Portable Generation Components are usually mechanically compact and also costs less for the repair or services as opposed to tall generators.
- Prompt Execution: They attend to emergencies aloud play without any major construction works.
Disadvantages of Portable Generators
- Reduced Energy Production: One of the disadvantages of portable generators is that they have less power output relative to Stationary Generators. As such, one cannot use them for powering large houses or for multiple heavy appliances simultaneously.
- Running Duration: Most of the portable generators do have small tanks, which means they keep on replenishing the fuel due to keen usage for long hours.
- Sound Pollution: Many portable generators, when on, operate while producing a lot of noise, disturbing the environment, especially neighbourhoods, or even if it is during camps.
- Health and safety issues: There is an increased risk when one does not use or place these machines properly, chances of one getting poisoned by carbon monoxide, posing an electric shock, or even heating up can be high. They should mainly be used in open spaces.
- Weather Restrictions: Portable generators do not withstand extreme climatic conditions; therefore cannot be left in such conditions for long without being covered with something or some kind of sheltered area, usually during rains or snowfall.
- Servicing and Fueling: About their servicing, all these types of units count on rigorous servicing for efficiency, not forgetting proper storage of fuel, which at times can be a strain to some people.
- Ecological Issues: Gas-powered or diesel-fired portable generators are detrimental to the environment because of the pollution they cause during use.
All these benefits and limitations considered, the user has to make a proper choice as to whether installing a Portable Generator will be of use under the specific situation or need that one is in at that point in time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standby Generators
Advantages of Standby Generators
- State of Emergency Power Supply: Stationary Generators can assure a non-stop energy inflow in case the grid goes off and the critical machinery is alive. This is crucial, especially to those residing in areas that experience constant blackouts.
- Power Output Levels: Stand-alone generators have higher power output levels than portable ones, which can only be used for light, mid-sized or so-called portable consumers.
- Ease and Operation: These machines are affixed in their locations, wiring is done to the houses, and a power transfer switch is fitted such that the machine will start up automatically upon the onset of a power outage.
- Fuel Types: Most of the Standby units available on the market operate on propane or natural gas, which might be less harmful to the environment than gasoline or diesel. Natural gases, which contain methane and some other gases in low proportions, should be refueled.
- Ensure Longer Period of Operation: Stationary Generators may serve for quite a long period as a result of adhering to maintenance schedules in comparison to portable planting their best advantage there.
- Any Improvement on a Purchasable Property: For most buyers, having a home with a standby generator is an added advantage, and thus homeowners find the need to incorporate such a feature in their home.
Disadvantages of Standby Generators
- High Initial Costs: Stationary Generators are more costly at the start, and the prices range anywhere between $5,000-$15,000 logarithmically, including installation prices.
- Installation Requirements: Installation must be done by a professional, and this can be a little more than what the budget allows because of an electrician and a gas fitter.
- Maintenance Needs: There has to be maintenance done frequently enough to keep the machine in better shape; turn on, change oil, replace filters, and check battery and system.
- Noise Levels: Besides some portable generators, the standby ones being studied more at home are less noisy but quite audible while in operation, which may be an issue for accommodating consumers.
- Environmental Impact: Even though they are fueled by cleaner natural gas, the use of these generators still generates greenhouse gases and harms the environment in the long run.
- Dependency on Gas Supply: Generators using natural gas need an existing supply from the utilities, making them susceptible in case of a larger outage, which may encompass gas infrastructures.
Having these points in mind, one can consider if a stationary generator is appropriate for their expectations, financially as well as ecologically.
Limitations of Portable vs Standby Generators
However, some drawbacks should be taken into account about both portable and stationary generators:
- Limitations in terms of power and capacity: The power of a portable generator rarely exceeds 2,000 watts, and is commonly within the range of 1,000-10,000 watts, meaning it can move only very simple devices or tools. Stationary generators, on the contrary, are capable of outputting a much larger capacity, often up to 20,000 watts or more, but the cost of their purchase and running expenses is higher.
- Initial Costs and Maintenance: Portable generators are cheaper at the outset and cost between $500 and $2,000, so they are sufficient for emergencies or sporadic use. Nevertheless, they make it necessary to top up with gasoline now and then, hence the lifetime may be short. A standby generator is a cost that shall be incurred at the very beginning and is usually $5,000 to $10,000 in addition to recommendations for maintenance, which includes oil and filter changes and additional wear costs.
- Fuel Use and Storage: The Story Of Small Generators: Most small gensets use gasoline in filling and it is impossible to store it in the room in bulk as it is a dangerous good. Also, the availability of gasoline is not always easy in case of any calamity. The standby variety of gensets are commonly powered by natural gas, propane, or both, which tend to be cleaner for the environment and more adaptive to longer power cuts; even so, they still need a constant fuel supply via pipeline.
- Movement and Setup: It Mobile generators are portably designed allowing utilisation to lots of different sites and they can be carried around at home with much ease, whereupon they can easily address power supply issues but, they also allow limited operation since they make quite a noise and are limited to the fuel tank capacity. Conversely, standby home generators do not require any external handling and turn on by themselves when the power goes out, but they are only fixed at one position, adding to the complexity of the design by requiring a technician to fit.
- Engine Noise and Eco-Productivity: According to the principles of mechanics, portable generators will be regarded as problematic to use for a long time within homes in that they make quite some noise, especially when exceeding 70db levels during operation. Both types of generators contribute to the production of smoke. However, some of the latest standby units are usually better in terms of energy consumption and emission concerns relative to the older portable models.
- Switching Systems Application: Connecting portable generators usually involves manual operations that take time, such as changing systems that power the given structure through what is a transfer switch. On the other hand, standby generators come on within seconds of an outage, providing uninterrupted power as long as the power and gas network it relies on is appropriately built.
So, all things considered, it is fair to say that a particular type of generator would meet specific demands, for that cuts down the range to the most appropriate, taking into consideration the cost, usage, and extent of the power during missions, as well as the installation concerns.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs

The choice of a generator is mainly individual, based on the expected load, some planning cost, and also on how frequently the generator will be used. Where the need for power is short-term/occasional, such as in camps or simply running a few household appliances, a portable generator is more affordable and convenient. However, if there is a need for power backup at home or to run some critical equipment for a long period, one must consider the purchase of a stationary generator. They come with automatic start and stop features and do not require much effort to operate.
Before proceeding with any other aspect, try and analyse what wattage is necessary to power the essential appliances or systems. It is equally important to know the cost of installation, the kind of fuel they use, and how easy or difficult it is to maintain them. It’s recommended to stick to purchasing only from established manufacturers and check if the fitting generator meets all the required specifications.
Assessing Your Power Requirements
Any time you are assessing power needs, it is crucial that you note down the total wattage it takes to operate the most important appliances or systems available in the house. The first step is to list all the key appliances that are most likely to be used in the house during a power outage, such as a refrigerator, heating/cooling systems, light sources, medical devices, and modes of communication. Identify the wattage of each of these appliances from the labels or if possible the instruction leaflet of the appliance itself and then estimate the starting watts and the running watts of each appliance, since some machines, such as refrigerators and air conditioners, have a high starting wattage before they stabilize.
To illustrate, a common refrigerator would consume approximately 600 running watts but might need up to 1200 starting watts alone. On the other hand, if we compare air conditioners, the general range of consumption is between 2000 watts and 5000 watts depending on the dimensions and efficiency of the appliance. Adding up these numbers will help you get the realistic level of power that you will require. Experts suggest that to cater for surges in power consumption, an additional 10-20% is be added to the calculated figures.
Also, note the kind of generator wattage that will be needed. For portable generators, the power output is for simple applications and ranges from 2000 to 8000 watts. For those who want more power, standby generators hold the capacity to generate power ranging from 10000-24000 watts to cover the whole house. Such calculations can also be done using online tools or using wattage calculators available from good power equipment supplies, which also help in locating the right generator equipment.
Evaluating Mobility and Flexibility Needs
It is important to identify how much you will need to move the generator around and how large it will be. If one is looking to purchase a portable generator, mobility is easily achieved since most models come with wheels and carrying handles. Such generators are suitable for places where power is used for short periods, including outdoors and in cases of minor emergencies. Portable generator units in a contemporary setting, can, for instance, be in the range of 50 to 300 pounds, depending on the power in watts that they supply, and they are fit for narrow spaces where they can be stored quickly, and they can be assembled fast.
Conversely, the stationary standby generators stay put, and power is available at will whenever the home experiences power outages. Along with their immobility, these start to outweigh the latter characteristics in terms of use for a longer period of time or frequently. Generators of this kind are usually hard-wired into home circuits, offering assistance without manual operation and they are able to handle a lot of additional load.
In contrast, smaller units such as portable building generators, which can range from 2,000 to 5,000 watts, are enough to use as a source of light and to run a fridge for instance. Stationary Generators that generate between 10,000 watts and 24,000 watts are more appropriate for powering air conditioning, appliances, and other devices necessary for large homes or businesses. While making filters regarding the source of electricity, it is possible to conclude which type of generator would be best to use in order to fulfill your requirement.
Budget Considerations and Recommendations
When one is buying a generator, it becomes necessary to match their economic abilities with the power output, functionalities, and most importantly, the overall projection of the generator in the long run. The prices of most portable generators that can power very crucial appliances in houses in cases of short blackouts or even going camping, cost less than $500-$1500 are very economical. Similarly, if you need higher power low noise and greater fuel economy inverse generators are the best option going within a range of $1,000–$3,000, specifically design for delicate electronic devices or prolonged working hours.
Stationary Generators or rather generators that are powered by motors are more expensive than other types costing $3,000-$10000 (excluding installation costs). Such generators use the incertion system whereby the power goes off; the generators come on automatically fulfilling the electrical supply for the whole house or business. Standby generator installations, however, can cost a further $2,000 to $5,000 depending on particular considerations such as installation of fuel lines or upgrade of electrical panels.
Therefore, for those who cannot afford brand new equipment, suggest refurbished or barely used machines from trusted brands, which can serve as decent options without getting ripped off. It is also equally important to consider the service cost as well as the fuel consumption. All these because if they are high, then it adds to the cost of using the generator in the long run. For example, diesel generators may cost more in the beginning, but they are more fuel-efficient and last longer than gasoline ones. Lastly, brands and shops sometimes offer seasonal discounts and installment credits enabling customers who wish to purchase high-end units with more features such as monitoring ones, longer running time, et cetera, to do so at an affordable cost.
By researching and considering these factors, you will be able to find the best generator for your needs in terms of performance, reliability, and cost.
Summary of Portable Generator and Stationary Generator

Compact generators are portable devices used as power source for a limited period. They fit applications of relatively short duration, such as providing power for construction equipment, camping, or emergency power for a few hours. Such generators are cheap, but they are operated manually by setting them up and refueling.
Stationary Generators on the other hand or standby type are fixed electrical equipment that comes on automatically when there is no power. It provides power for domestic or commercial appliances that need a continuous supply of power over a long period. Although their costs are higher up front and they need to be installed professionally, such generators are more convenient, more dependable and have a greater power output.
In order to make a choice, the nature of the power need and how long it is required, the cost of buying and maintaining the equipment, and the convenience in operating the equipment should be taken into account. These types have different purposes, therefore the choice is to be made on the basis of need.
Final Thoughts on Portable vs Standby Generators
Stationary Generators have earned the trust of many consumers for good reasons. Not all the units that can fit the bill are naturally within an easy reach of every person. Stationary horses go for less than a thousand dollars and are suitable for shorter durations and right-size items like refrigerators, plus lights and other small gadgets in the absence of power. But since mostly out put powers vary from as low as 1k, average being around 8K, as all the appliances fit inside it with ease, this type of appliance will not be effective.
Stationary Generators on the other hand, are more appropriate for issues of prolonged electricity use. Recent statistics suggest that on average, standby generators can produce between 7 and 24K+ watts of energy, which is perfect for meeting high-power requirements, providing power for the entire home or business. Furthermore, while the cost of standby generators ranges from $5,000 to $10,000, including the installation process, they operate without needing interference and a backup fuel such as natural gas or propane to ensure continuation of power in case of extended temperature changes. In addition, the development of standby systems has also made it possible for them to be less noisy and be more energy saving, which has also made them more preferable.
Finally, considering if you can use a particular generator will involve looking at the amount of power you need, the costs and maintenance now and later, respectively, and how often you will need to use it. Different generators are designed for different reasons so not everyone will understand which one works better for them but at least there will be a generator to keep the lights on during any blackout.
Key Takeaways for Informed Decision Making
- Analyzing and Calculating Your Power Consumption
Before anything else, it is important to know how much power you need. For instance, every home has a few essential sources including refrigerators, overhead lights, or even a medical device that may need 3000 up to 7000 watts. Whereas for businesses, the wide spectrum of operations leads to power consumption that can easily exceed 20k watts or even more.
- Look for Various Power Sources
The Sunny Side of Every Coin Has a Power Source, and that is the type of fuel that has been used to construct the particular generator. Gasoline generators are relatively cheap, accessible in the market, and however not so suitable for instances that require extensive storage periods due to the deterioration of fuel. There is propane, which offers a cleaner form of energy with longer shelf lives, and lastly, diesel, which is more efficient and suitable for high-duty use.
- Evaluate Energy Efficiency
Today’s generators are more efficient on the of energy usage, with some portable versions reducing fuel consumption by as much as 30% from the old versions. Choose the models fitted with advanced inverter features that give a stable power supply with maximum efficiency.
- Noise Levels Matter
Many people prefer to have low-noise generators, especially when they use them at home. Some of the newer generator designs may produce a noise level of 65 decibels, which is more like music playing in the background and very helpful for additional comfort.
- Cost Preparation
Some generators are more expensive than others, with the small handy ones being cheaper at about $500 while the larger type called stationary generators, would cost North of $10,000. In addition, it is worth incorporating additional costs such as fuel usage, servicing, and replacement if necessary.
- Being Prepared
Purchasing a generator minimizes the disruptions in case of prolonged power interruptions due to disasters and collapses in the grid. Statistics reveal that some regions experienced an increase in the number of power interruptions by 64% within the last twenty years depicting the need for an alternative source of power.
- Environmental Considerations
Newer models were developed to meet stringent emissions requirements, hence reducing their effect on the environment. Pick generators that are EPA compliant – or better, meeting CARB standards – because you want to minimize your impact on the environment.
These are the key aspects that will need to be considered for you to make an informed choice of the generator that will address your current power needs and the possible future ones with maximum benefits from the purchase.
Expert Advice for Generator Selection
When buying a generator, the one you choose must match the power needs, cost, and purpose the generator is meant for. Below are some of the specific factors and thoughts that should be of help in making the choice:
- Assess Your Power Requirements
Make a list of all the appliances or devices that will be used with the generator and add up the total wattage output. For instance, a refrigerator draws about 600 watts of power; a window unit air conditioner may use 1,500 watts. Target for a power overrun of up to 20-25% above the total wattage estimate to be able to cater for any power in rush or load switching.
- Mobile Versus Rotary Stationary Generators
Portable generators in a way, are cheap and flexible, as small models are priced as low as $500. However, they are portable, meaning that they have to be manually set up and refueled whenever the tank runs dry. On the other hand, apart from being more expensive, at times upwards of $3,000, standby generators eliminate refilling headaches and provide more power, making them suitable for companies or homes over a long period.
- Fuel Kind and Fuel Economy
Generators are fueled by gasoline, diesel engines, propane, or natural gas. Gasoline models are the most common but tend to consume more fuel and have limited running time. Diesel models are more economical on fuel, whereas propane and natural gas types are ‘greener’ and more economical in terms of use, but can include harsh initial costs, depending on the availability in your area.
Understanding these constraints and the needs at your disposal will help you in deciding on the best generator. The one that will be the enhance the utilization of resources and avert any inconveniences during power outages.
Reference Sources
-
Electrical Power Generator Use and Procurement Guidance
A document from Syracuse University discussing the classification and use of portable and stationary generators, including regulatory considerations.
View the document -
Remember Safety with Standby Generators on the Farm
A resource from the University of Kentucky Extension Service explaining the use of standby (stationary) generators for emergency power, with safety considerations.
Access the resource -
Portable Generator Safety Information
A guide from the New Hampshire Fire Marshal’s Office detailing the differences between portable and stationary generators, including safety and usage tips.
Explore the guide -
How to Choose a Generator for Refrigerator? Expert Tips
A resource from Rice University discussing the types of generators, including portable and stationary, for residential use.
Read the article -
Generator Safety Tips
A guide from the Town of Burlington, Connecticut, providing safety tips and operational differences between portable and stationary generators.
View the guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between portable generators and standby generators?
The main difference between portable generators and standby generators lies in their design and intended use. Portable generators are designed for mobility, allowing users to transport them easily to different locations, making them ideal for camping or temporary power needs. In contrast, standby generators are permanently installed and automatically kick in during a power outage, providing a seamless power supply to your home. Standby generators can power your entire home, while portable generators typically supply power for specific appliances. When choosing between these options, consider your power needs and whether you prefer the flexibility of a portable generator or the reliability of a standby generator.
What are the pros and cons of portable vs standby generators?
When evaluating the pros and cons of portable vs standby generators, it’s essential to consider various factors. Portable generators are generally more affordable and versatile, as they can be used for multiple purposes, such as powering tools at a job site or providing backup during camping trips. However, they often require manual setup and may not provide enough power for larger appliances during an extended power outage. On the other hand, standby generators are designed for whole-home backup power and can automatically start during outages, ensuring your home keeps running without interruption. The downside is that standby generators typically have higher upfront costs and require professional installation. Assess your needs to determine which generator is best for your situation.
How to choose the right generator for your needs?
Choosing the right generator for your needs involves assessing several key factors. First, consider the power requirements of your home or devices; a home backup generator can provide the necessary wattage for essential appliances during an outage. Next, think about whether you need a portable generator for temporary use or a standby generator for whole-house coverage. It’s also crucial to evaluate the fuel type—fossil fuel portable generators may be less convenient than dual fuel generators that can switch between natural gas and propane. Lastly, factor in your budget for both purchase and installation, especially for standby generators that require a fixed installation. By weighing these considerations, you’ll find the generator that’s right for your specific circumstances.
What types of generators are available?
There are several types of generators available, each designed for specific applications. Portable generators are popular for their flexibility and are best for temporary power needs, such as outdoor events or construction sites. Standby generators, on the other hand, are fixed installations that automatically activate during power outages, providing reliable backup for your entire home. Additional options include inverter generators, which are quieter and more efficient for sensitive electronics, and dual fuel generators that can operate on both gasoline and propane. When exploring generator options, consider factors such as power output, portability, and fuel type to find the best fit for your requirements.
Are portable generators or standby generators better for home use?
When determining whether portable generators or standby generators are better for home use, it largely depends on your specific needs. Standby generators are designed to provide seamless power during outages, automatically activating and powering your entire home, which is advantageous for those who prioritize convenience and reliability. In contrast, portable generators might be more suited for occasional use, such as powering tools or appliances during outdoor activities or short outages, but require manual operation and setup. If you experience frequent extended power outages, a home backup generator may be the best choice. Ultimately, assess how often you lose power and what appliances you need to support to make the right decision.
What is the best generator for an extended power outage?
For an extended power outage, a standby generator is often the best solution due to its ability to provide whole-home backup power automatically. Standby generators are designed to kick in as soon as a power failure is detected, ensuring that essential systems like heating, cooling, and refrigeration remain operational. While portable generators can also be used, they typically require manual setup and may not supply enough electricity to power larger appliances simultaneously. If you prefer a more flexible option, dual fuel generators can provide backup power for critical devices and can switch between natural gas and propane. Consider your power needs and how frequently you experience outages to determine which generator is right for you.
